Did you know?
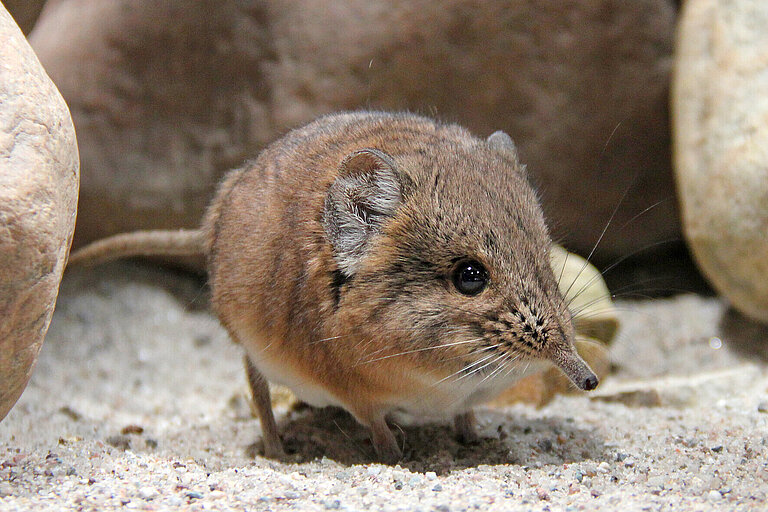
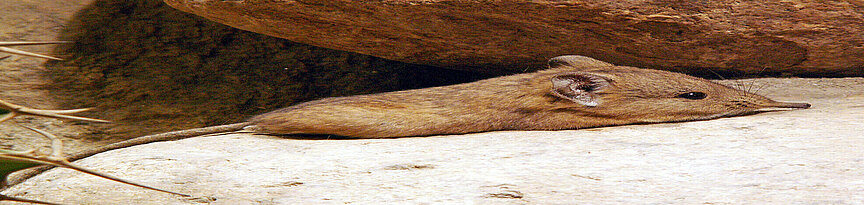
Short-eared elephant shrews are diurnal (active by day) and live as individuals or in pairs. They use their long, flexible noses among other things to hunt for insects and arachnids. On their territory they make a series of cleared pathways through the undergrowth, leading to hiding places or hunting grounds. The pathways are stored like maps in the animal’s memory and are kept meticulously clean. When danger arises
they know exactly which is the quickest route to the closest hiding place.
Characteristics
| Classification | Order: elephant shrews, family: macroscelididae |
|---|---|
| Diet | Ants, termites, spiders, eggs, small vertebrates, seeds and fruits |
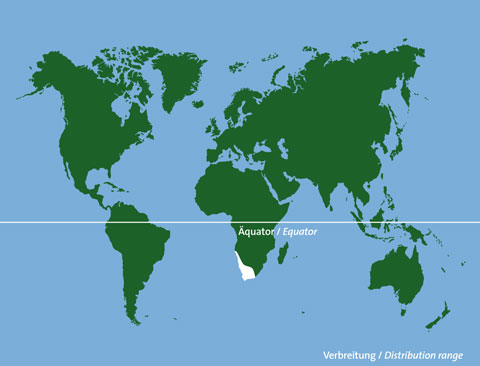
| Habitat | Dry steppes with thorn bushes, scree and shrubs, semi-deserts, stone deserts and deserts |
| Reproduction | Mating all year round; gestation period: 56–61 days, 1–2 nidifugous offspring; suckling period: 3 weeks; sexual maturity at 3–4 months; maximum age: over 8 years |
Status according to Red List
More information you will get on the web page of the IUCN Red List.